Parts of Speech Serie – Prepositions
Prepositions can be difficult for EFL students. Why? Because there are barely any rules telling us when to use which preposition, and there are several different types!
Unfortunately, the only way to learn prepositions is by looking them up in a dictionary, reading, and memorizing their most common uses. But first, we need to know what they are and what they do.
Prepositions are used to connect nouns, pronouns, and/or phrases in a sentence to indicate their relation, to tell how they are related in space, in a place, in time, or as part of a thought or process. There are three main different types of prepositions:
- Prepositions of Place
on – expressing location on a surface:
- On the table
- On the rug
- On the floor
at – expressing location at a physical point:
- At the end of the lane
- At the door
- At the corner
across – expressing a position or orientation:
- Across the table
- Across the room
over – positioned directly upward from:
- Over the stove
- Over the patio
in – positioned inside of something:
- In the room
- In my pocket
- In the building
double prepositions – two words combined together to create one preposition:
- Into
- Within
- Upon
- Onto
Prepositions of Place examples:
- “The bottle of wine is on the table.”
- “We bought this TV at the electronics store.”
- “At the restaurant, I sat across the table from my friend.”
- “We are lucky to have a roof over our heads.”
- “I think your beach towel is still in the suitcase.”
- “My little sister came into my room and jumped onto the bed while I was sleeping.”
- “As you can read within the details of the story, the theme was based upon two moral principles.”
- Prepositions of Time:
on – used for days and dates:
- On Wednesday
- On the 10th of January
- On Christmas
at – indicates a specific hour:
- At 3:30 in the afternoon
- At noon
in – indicates an amount of time or period of the day:
- In the morning
- In twenty minutes
until – indicates that an activity will continue up to a particular time:
- Until tomorrow
- Until noon
during – indicates that an activity occurs simultaneously with a particular period of time:
- During the winter
- During the meeting
for – indicates the duration of an activity:
- For 2 hours
- For a decade
from – to – indicates the beginning and ending of a period of time:
- From Monday to Friday
- From 2001 to 2007
Prepositions of Time examples:
- “At five o’clock, we will have been working forten hours.”
- “In the morning, I sleep until”
- “He did his homework during the show.”
- “They have baseball practice from three to four every day.”
- “On Tuesdays, I go golfing with my friends.”
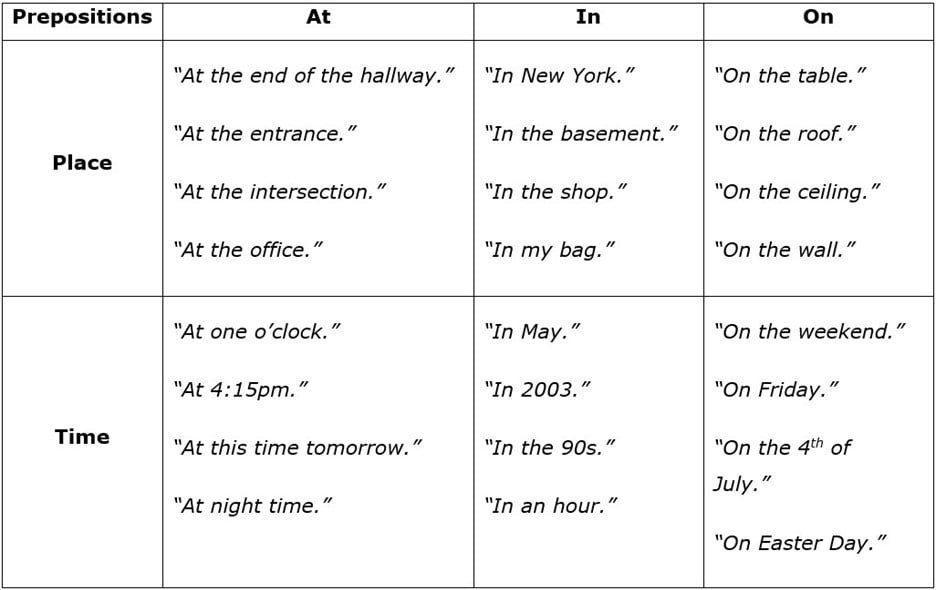
The following chart outlines specific examples of the use of the common prepositions: “at,” “in,” and “on” in the categories of both place and time:
- Prepositions of Movement:
to – indicates motion towards a specific destination (i.e., place, event, person, position, etc.)
- “I went to the bank.”
towards – indicates a more vivid sense of movement in a particular direction
- “He was walking menacingly towards”
through – indicates movement within a delimited space
- “The subway went through the tunnel.”
- “The scissors sliced right through the fabric.”
into – indicates movement from the outside to the inside of something or movement causing something to hit something else
- “I got into my car and left.”
- “The car bumped into the back of the car in front of it.”
across – indicates movement from one side of something to the other or when something stretches over a surface
- “He swam across the river.”
- “The stars stretch acrossthe night sky as far as I can see.”
over – used when something moves above or on top of the surface of something
- “The dog jumped over the couch.”
- “We couldn’t sleep because the sound of the plane flying overthe house was very loud.”
along – indicates linear movement
- “We drove along the coast all the way to the South.”
on – used to describe movement in the direction of a surface
- “I sprinkled some salt on the steak.”
- “The rain falling on the roof kept me from sleeping.”
In addition to the three main categories of prepositions, there also exist other types of prepositions, including the following:
Compound Prepositions – two-word prepositions
- out of
- in front of
- next to
- on top of
For example:
- “The soccer game was held in front of a huge crowd.”
- “A bird landed on top of a stack of books.”
- “I can’t get that song out of my head.”


So nit
So nice
very informative and precise article.