Parts of Speech Serie – Adjective
Adjectives describe nouns in various ways:
- What kind? (Chinese food)
- How much/many? (several people)
- What color? (the blue sky)
- What size? (a big dog)
- What texture? (a hardshell)
- What emotion? (a happy moment)
There are five different types of adjectives which are classified by the different aspects of the noun they describe:
- Quality – Used to describe characteristics of a noun:
- humble
- generous
- big
- tiny
- beautiful
- ugly
For example:
- “Dubai is a large city with many skyscrapers.”
- “Mary is a beautiful woman.”
- Quantity – Shows the amount of the noun or pronoun in relative or whole terms:
- most
- many
- much
- few
- all
- numerous
- enough
For example:
- “There are a few pieces of chicken”
- “Several people came to my party.”
- Number – Shows the number of nouns and their place in an order
Definite Numeral Adjective – exact number of nouns or the order of the noun:
- One
- Three
- Twenty-two
- Forty-Three
- First
- Third
- Twenty-second
- Forty-third
For example:
- “She was the first girl to score three goals in one game.”
- “Ten of the gymnasts came in second place in all five”
- Demonstrative – Indicates a particular noun or pronoun:
- this
- that
- these
- those
You might be thinking right now, “Wait, I thought I saw these words listed under Demonstrative Pronouns! What the heck?” and you’re right, you did!
If you haven’t seen the article about pronouns, click here.
However, demonstrative pronouns are used to REPLACE another noun or noun phrase, whereas demonstrative adjectives are used to INDICATE, or POINT OUT specific items.
Demonstrative pronouns always stand on their own, while demonstrative adjectives are ALWAYS followed by the noun they describe. Take a look at the following chart comparing the two:
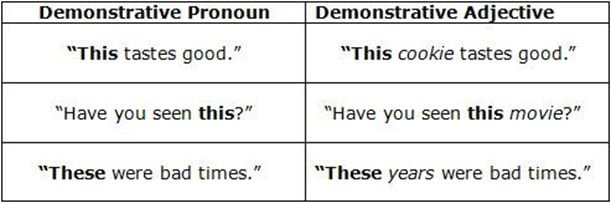
More examples of Demonstrative Adjectives:
- “That car is the one I saw parked in front of my house.”
- “Do you think this dress is nice?”
- “I want to buy those sunglasses.”
- “These cookies are delicious.”
- Interrogative – Asks questions about nouns or in relation to nouns:
- What
- Which
- Whose
But weren’t these words also listed under Interrogative Pronouns? Interrogative pronouns differ from interrogative adjectives because the pronouns actually stand in for the missing information (the noun or noun phrase), whereas interrogative adjectives are followed by the noun they are referring to.
Take a look at the following chart comparing the two:

More examples of Interrogative Adjectives:
- “What assignment did I miss out on?”
- “Which book is your favorite?”
- “Whose pen is this?”

